Baked potatoes with some kind of topping are a popular snack, takeout option, and even a meal. But what kind of nutrition are we actually getting when we choose these options?
While potatoes are fairly nutritious on their own, the toppings we add to a baked potato can either boost their nutritional properties or add excess fat, salt, and calories without providing much extra nutrition.
In this article, we explore how different types of toppings impact the nutritional properties of baked potatoes. For each option, we’ll provide data on their calorie, carbohydrate, fat, protein, and sodium composition so you can see how the fat, calorie, and salt content can change depending on the topping.
We’ll also look at the top five vitamins and minerals present in the highest concentrations.
All nutrition data represents typical values and, unless otherwise stated, is sourced from the USDA’s FoodData Central database.
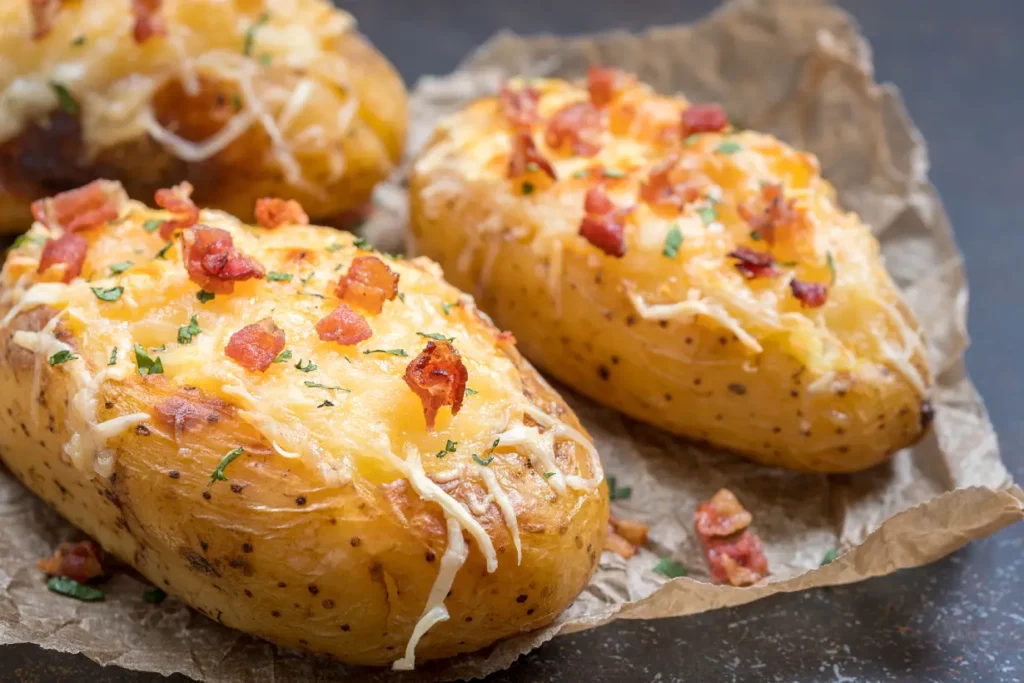

Table of contents
- 1) Baked Potato (Plain)
- 2) Baked Potato Topped With Bacon
- 3) Baked Potato Topped With Baked Beans
- 4) Baked Potato Topped With Brocolli Cheese
- 5) Baked Potato With Butter
- 6) Baked Potato With Cheese
- 7) Baked Potato With Chili
- 8) Baked Potato Topped With Sour Cream
- 9) Baked Potato With Tuna Mayo Topping
- Comparison Table: Baked Potato Nutrition Facts By Type of Topping
- Summary
1) Baked Potato (Plain)
First, let’s examine the nutritional values of a plain baked potato to establish a baseline for comparison with other options.
Typical Ingredients
- 1 medium (285g) baked potato, eaten with peel
- 1.3 grams of salt
Nutrition
- Calories: 265 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 60 g
- Fiber: 6.27 g
- Sugars: 3.36 g
- Fat: 0.37 g
- Saturated fat: 0.10 g
- Monounsaturated fat: 0.01 g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 0.16 g
- Protein: 7.1 g
- Cholesterol: 0 mg
- Sodium: 530 mg
Top 5 Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin B6: 0.88 mg (52% DV)
- Copper: 0.33 mg (37% DV)
- Potassium: 1520 mg (32% DV)
- Vitamin C: 27.4 mg (30% DV)
- Folate, DFE: 79.8 mcg (20% DV)
As we can see, plain baked potatoes are primarily a source of carbohydrates. They are relatively low in calories and provide an excellent source of vitamin B6, copper, potassium, vitamin C, and folate.
2) Baked Potato Topped With Bacon
Here’s the nutritional information for a baked potato with bacon as one of the toppings.
Typical Ingredients
According to USDA data, a bacon-topped baked potato typically contains the following ingedients:
- 1 medium (285g) baked potato, eaten with peel
- 1.3 grams of salt
- 1 tbsp (15g) butter
- 1 ounce (28g) Cheddar cheese
- 30 grams sour cream
- 8 grams (1 slice) pan-fried bacon
Nutrition
- Calories: 504 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 53.8 g
- Fiber: 5.36 g
- Sugars: 3.91 g
- Fat: 26.1 g
- Saturated fat: 14.1 g
- Monounsaturated fat: 6.01 g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 1.37 g
- Protein: 14.9 g
- Cholesterol: 75.6 mg
- Sodium: 810 mg
Top 5 Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin B6: 0.82 mg (48% DV)
- Copper: 0.31 mg (34% DV)
- Potassium: 1400 mg (30% DV)
- Phosphorus: 337 mg (27% DV)
- Vitamin C: 23.6 mg (26% DV)
Benefits
- A baked potato topped with bacon (and cheese) offers significantly more protein (14.9g) compared to a plain baked potato (7.1g).
- Slightly higher levels of calcium and B vitamins.
Potential Drawbacks
- High in saturated fat and sodium.
- One of the highest-calorie toppings when bacon, cheese, sour cream, and butter are all added, as per the USDA’s typical ingredients data.
3) Baked Potato Topped With Baked Beans
Baked Beans are a popular choice for a baked potato topping. Let’s examine how they impact the nutritional profile compared to a plain baked potato.
Typical Ingredients
- 1 medium (285g) baked potato, eaten with peel
- 1.3 grams of salt
- 1/2 cup (127g) Baked Beans
Nutrition
- Calories: 384 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 86.85 g
- Fiber: 11.48 g
- Sugars: 13.47 g
- Fat: 0.84 g
- Saturated fat: 0.19 g
- Monounsaturated fat: 0.13 g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 0.31 g
- Protein: 13.13 g
- Cholesterol: 0 mg
- Sodium: 966 mg
Top 5 Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin B6: 0.99 mg (58% DV)
- Copper: 0.51mg (57% DV)
- Potassium: 1804.48 mg (38% DV)
- Zinc: 3.93 mg (36% DV)
- Vitamin C: 27.4 mg (30% DV)
Sources
Benefits
- A half-cup serving of Baked Beans as a baked potato topping adds 119 calories and approximately doubles the fiber and protein content
- The vitamins and minerals present in the highest concentrations include vitamin B6, copper, potassium, zinc, and vitamin C.
- The significant increase in the zinc content of the meal comes from the beans.
Potential Drawbacks
- Adding beans roughly doubles the sodium content of the meal.
4) Baked Potato Topped With Brocolli Cheese
Here’s what a baked potato topped with brocolli in cheese sauce provides nutritionally.
Nutrition
- Calories: 489 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 65.29 g
- Fiber: 7.20 g
- Sugars: 4.0 g
- Fat: 20.66 g
- Saturated fat: 8.26 g
- Monounsaturated fat: 4.18 g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 4.96 g
- Protein: 14.83 g
- Cholesterol: 29 mg
- Sodium: 873 mg
Top 5 Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin B6: 1.57 mg (92% DV)
- Vitamin B12: 2.02 mg (84% DV)
- Vitamin C: 37.09 mg (41% DV)
- Copper: 0.37 mg (41% DV)
- Potassium: 1654 mg (35% DV)
Source: NCC Food and Nutrient Database
Benefits
- Topping baked potatoes with broccoli in cheese sauce provides significantly more B vitamins, calcium, vitamin C, and vitamin K.
- Provides a significant amount of vitamin B12.
- Provides slightly more fiber and more than doubles the protein content.
Potential Drawbacks
- Adding cheese sauce significantly increases saturated fat and nearly doubles the sodium and calorie content of the meal.
5) Baked Potato With Butter
Let’s now examine the nutritional changes from topping a baked potato with butter.
Typical Ingredients
- 1 medium (285g) baked potato, eaten with peel
- 1.3 grams of salt
- 1 tbsp (15g) butter
Nutrition
- Calories: 394 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 63.0 g
- Fiber: 6.62 g
- Sugars: 3.59 g
- Fat: 13.3 g
- Saturated fat: 7.25 g
- Monounsaturated fat: 2.66 g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 0.56 g
- Protein: 7.59 g
- Cholesterol: 37.8 mg
- Sodium: 639 mg
Top 5 Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin B6: 0.93 mg (55% DV)
- Copper: 0.35 mg (39% DV)
- Potassium: 1600 mg (34% DV)
- Vitamin C: 28.7 mg (32% DV)
- Folate, DFE: 85 mcg (21% DV)
Benefits
- For individuals specifically seeking to increase their calorie and fat intake, adding butter to a baked potato is an easy way to boost calories.
- Butter provides a small amount of fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin A, though these are present in relatively low concentrations.
Potential Drawbacks
- The addition of butter has no significant impact on the protein, fiber, vitamin, and mineral content of the baked potato.
- Butter adds around 130 calories and a large amount of saturated fat compared to a plain baked potato.
6) Baked Potato With Cheese
Adding cheese to a baked potato adds a broader range of nutrients compared to butter.
Typical Ingredients
- 1 medium (285g) baked potato, eaten with peel
- 1.3 grams of salt
- 1 tbsp (15g) butter
- 1 ounce (28g) Cheddar cheese
- 30 grams sour cream
Nutrition
- Calories: 482 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 54.9 g
- Fiber: 5.36 g
- Sugars: 4.0 g
- Fat: 24.2 g
- Saturated fat: 13.6 g
- Monounsaturated fat: 5.06 g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 0.97 g
- Protein: 12.9 g
- Cholesterol: 69.3 mg
- Sodium: 709 mg
Top 5 Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin B6: 0.80 mg (47% DV)
- Copper: 0.302 mg (34% DV)
- Potassium: 1400 mg (30% DV)
- Vitamin C: 24.3 mg (27% DV)
- Phosphorus: (25% DV)
Benefits
- Adding cheese provides high amounts of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin A.
- Nearly doubles the protein content compared to a plain baked potato.
Potential Drawbacks
- The addition of cheese, sour cream, and butter increases the fat, saturated fat, and calorie content significantly. This isn’t inherently negative but depends on the overall diet context.
It should be noted that the USDA for a typical cheese-topped baked potato assumes it includes butter and sour cream. A homemade version using only cheese would contain fewer calories and less fat.
7) Baked Potato With Chili
Here’s how topping a typical baked potato with chili changes the nutritional profile.
Typical Ingredients
- 1 medium (285g) baked potato, eaten with peel
- 1.3 grams of salt
- 1 tbsp (15g) butter
- 1 ounce (28g) Cheddar cheese
- 60 grams of chili with meat
Nutrition
- Calories: 450 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 54.6 g
- Fiber: 6.62 g
- Sugars: 3.56 g
- Fat: 19.6 g
- Saturated fat: 10.6 g
- Monounsaturated fat: 4.43 g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 0.83 g
- Protein: 15.3 g
- Cholesterol: 59.8 mg
- Sodium: 816 mg
Top 5 Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin B6: 0.81 mg (48% DV)
- Copper: 0.35 mg (39% DV)
- Potassium: 1390 mg (30% DV)
- Vitamin C: 25.2 mg (28% DV)
- Phosphorus: 315 mg (25% DV)
Benefits
- More than double the protein content compared to a plain baked potato.
- Higher concentrations of B vitamins, iron, and zinc.
Potential Drawbacks
- Significantly more calories, saturated fat, and sodium than a plain baked potato.
8) Baked Potato Topped With Sour Cream
How does topping a baked potato with sour cream change its nutritional properties?
Typical Ingredients
- 1 medium (285g) baked potato, eaten with peel
- 1.3 grams of salt
- 1 tbsp (15g) butter
- 30 grams sour cream
Nutrition
- Calories: 413 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 58.9 g
- Fiber: 5.98 g
- Sugars: 4.25 g
- Fat: 17.2 g
- Saturated fat: 9.65 g
- Monounsaturated fat: 3.5 g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 0.74 g
- Protein: 7.78 g
- Cholesterol: 47.2 mg
- Sodium: 595 mg
Top 5 Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin B6: 0.85 mg (50% DV)
- Copper: 0.31 mg (36% DV)
- Potassium: 1500 mg (32% DV)
- Vitamin C: 26.1 mg (29% DV)
- Niacin: 3.85 mg (24% DV)
Benefits
- The addition of sour cream doesn’t significantly impact the protein, fiber, vitamin, or mineral profile of a baked potato. However, it may benefit individuals seeking to increase their fat and calorie intake.
Potential Drawbacks
- Sour cream adds a significant amount of calories, saturated fat, and sodium.
9) Baked Potato With Tuna Mayo Topping
Here’s how topping a baked potato with tuna mayonnaise impacts the nutritional profile.
Typical Ingredients
- 1 medium (285g) baked potato, eaten with peel
- 1.3 grams of salt
- 1/2 can (80.5g) light tuna, canned in oil, drained
- 1 tbsp (13.8g) mayonnaise
Nutrition
- Calories: 528 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 60.07 g
- Fiber: 6.27 g
- Sugars: 3.43 g
- Fat: 17.69 g
- Saturated fat: 3.03 g
- Monounsaturated fat: 4.85 g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 8.8 g
- Protein: 32.14 g
- Cholesterol: 21.19 mg
- Sodium: 973 mg
Top 5 Vitamins and Minerals
- Selenium: 66 mcg (120% DV)
- Niacin: 14.6 mg (91% DV)
- Vitamin B6: 0.97 mg (57% DV)
- Copper: 0.39 mg (43% DV)
- Phosphorus: 468.81 mg (38% DV)
Sources
Benefits
- Adding tuna as a topping, which is a lean protein source, significantly increases the protein content.
- Tuna increases the content of many vitamins and minerals, particularly selenium and niacin.
Potential Drawbacks
- The addition of mayonnaise contributes a large number of calories and high sodium content without providing much extra nutritional value.
Comparison Table: Baked Potato Nutrition Facts By Type of Topping
Below is a comparison table showing the basic calorie and macronutrient composition for different varieties of baked potatos.
| Baked potato variety | Calories | Carbohydrates | Fat | Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baked potato with baked beans | 384 kcal | 86.85 g | 0.84 g | 13.13 g |
| Baked potato with bacon | 504 kcal | 53.8 g | 26.1 g | 14.9 g |
| Baked potato with broccoli cheese | 489 kcal | 65.39 g | 20.66 g | 14.83 g |
| Baked potato with butter | 394 kcal | 63.0 g | 13.3 g | 7.59 g |
| Baked potato with cheese | 482 kcal | 54.9 g | 24.2 g | 12.9 g |
| Baked potato with chili | 450 kcal | 54.6 g | 19.6 g | 15.3 g |
| Baked potato with sour cream | 413 kcal | 58.9 g | 17.2 g | 7.78 g |
| Baked potato with tuna mayo | 528 kcal | 60.07 g | 17.69 g | 32.14 g |
| Plain baked potato | 265 kcal | 60.0 g | 0.37 g | 7.1 g |
Summary
As this guide demonstrates, the nutritional values of a baked potato can significantly differ depending on the chosen topping.
Some toppings provide substantial amounts of protein, while others mainly increase fat and calorie content.
If taste is the only consideration, all these topping varieties may be appealing.
However, for specific dietary goals, such as “low sodium” or “high protein,” there are noticeable differences between these options. Hopefully this guide will help you make informed decisions based on your dietary preferences and goals.