Sometimes referred to as “the sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D is an essential fat-soluble vitamin.
Vitamin D has great importance for human health, and it plays a role in blood pressure regulation and immune health, among many other functions (1).
While sunlight is the most recognized way of getting vitamin D, numerous foods provide a good amount of this nutrient.
This article takes an in-depth look at thirty foods that provide high vitamin D content.
For reference, the current reference daily intake (RDI) for vitamin D is 600 IU (15 mcg) for adults. However, this falls to 400 IU (10 mcg) for children under 12 months old and rises to 800 IU (20 mcg) for adults over the age of 70 (2).
The FDA has set a daily value (DV) for vitamin D of 20 mcg (3).
This article’s source of all nutritional values is the USDA FoodData Central Database.

1) American Cheese (Fortified)
Otherwise known as sliced cheese, American cheese is a type of processed cheese product sold in individually packaged slices.
The ingredients of American cheese include milk, milk protein, cheese, salt, and preservatives.
Per slice serving, American cheese provides 1.36 mcg of vitamin D, equal to 7% of the recommended daily value (3).
| American Cheese Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 slice (21g) | 1.36 mcg | 7% DV |
| 100 grams | 6.5 mcg | 33% DV |
2) Atlantic Mackerel
Not only is mackerel a popular fish, but it is also one of the most nutrient-rich food options.
Atlantic mackerel is a good choice of fish as it contains high amounts of omega-3 and very low mercury concentrations.
Per 112-gram (raw weight) fillet, mackerel provides 16.1 mcg of vitamin D (4).
| Atlantic Mackerel Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 112-gram fillet | 18.0 mcg | 90% DV |
| 100 grams | 16.1 mcg | 81% DV |
Learn more about vitamin D in fish: 27 Fish Sources of Vitamin D
3) Beef Kidney
| Beef Kidney Serving Size | Vitamin D Amount | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| Per 100 grams | 1.1 mcg / 45 IU | 8 % |
| Per 4 oz (113g) | 1.2 mcg / 51 IU | 9 % |
Although not quite as popular as other cuts of meat, kidney meat tends to be a significant source of many vitamins and minerals.
On this note, a three-ounce (85g) serving of cooked beef kidney supplies 0.935 mcg of vitamin D (4).
Additionally, beef kidneys are an excellent source of protein, selenium, and B vitamins.
| Beef Kidney Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 3 oz (85g) | 0.935 mcg | 5% DV |
| 100 grams | 1.1 mcg | 6% DV |
4) Beef Liver
Beef liver is another nutrient-rich type of organ meat, and it is a source of most vitamins and minerals.
While the vitamin D content is not quite as high as some of the other nutrients liver provides, it still provides a decent amount.
A three-ounce (85g) serving of braised liver offers 1.02 mcg of vitamin D (5).
| Beef Liver Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 3 oz (85g) | 1.02 mcg | 5% DV |
| 100 grams | 1.2 mcg | 6% DV |
5) Bran Flakes
Many different cereal products are fortified with vitamin D voluntarily.
The Kellogg’s brand of Bran Flakes is one of these, and the cereal provides 1.36 mcg of vitamin D per cup (39g) serving (6).
| Kellogg’s Bran Flakes Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 39-gram cup | 1.36 mcg | 5% DV |
| 100 grams | 3.5 mcg | 18% DV |
6) Canned Pink Salmon
Canned pink salmon is one of the most convenient vitamin D-rich foods.
Per three-ounce (85g) serving, canned pink salmon provides 11.6 mcg of vitamin D (7).
| Canned Pink Salmon Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 3 oz (85g) | 11.6 mcg | 58% DV |
| 100 grams | 13.7 mcg | 69% DV |
7) Cheddar Cheese
Although only a relatively small amount, all cheese products contain varying amounts of vitamin D.
However, since Cheddar is one of the most popular types of cheese globally, it is one of the most common dietary sources.
Per ounce (28g) serving, Cheddar provides 0.17 mcg of vitamin D (8).
| Cheddar Cheese Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 oz (28g) | 0.17 mcg | 1% DV |
| 100 grams | 0.6 mcg | 3% DV |
8) Chicken Fat
Although we often think of animal fats as being just fat/extra calories, they contain a range of vitamins and minerals.
Among these vitamins and minerals, animal fats provide a small amount of vitamin D.
Per tablespoon (12.8g) serving, chicken fat contains 0.614 mcg of vitamin D (9).
| Chicken Fat Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 tbsp (12.8g) | 0.614 mcg | 3% DV |
| 100 grams | 4.8 mcg | 24% DV |
9) Cod Liver Oil
Cod liver oil is a cod-based dietary supplement marketed as a source of omega-3, vitamin A, and vitamin D.
Per teaspoon (4.5g) serving, cod liver oil has a vitamin D content of 11.2 mcg (10).
| Cod Liver Oil Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 tsp (4.5g) | 0.614 mcg | 3% DV |
| 100 grams | 250 mcg | 1250% DV |
10) Corn Flakes (Fortified)
Corn Flakes are another popular breakfast cereal fortified with vitamin D.
The Kellogg’s brand of Corn Flakes offers 1.01 mcg of vitamin D per 28-gram cup serving (11).
| Kellogg’s Corn Flakes Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cup (28g) | 1.01 mcg | 5% DV |
| 100 grams | 3.6 mcg | 18% DV |
11) Cremini/Chestnut Mushrooms (UV Exposed)
Mushrooms grown with exposure to sunshine or under UV lamps have natural vitamin D content.
Cremini mushrooms, also known as chestnut mushrooms, are among the most common UV-exposed mushroom varieties.
Furthermore, an 87-gram cup of cremini mushrooms provides an impressive 27.8 mcg of vitamin D (12).
| Cremini Mushroom Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cup (87g) | 27.8 mcg | 139% DV |
| 100 grams | 31.9 mcg | 160% DV |
12) Eggs
Eggs provide a broad range of essential nutrients, and vitamin D is among these.
While the amount may not be so high in just one egg, a two or three-egg omelet is a simple way to get a good amount of the vitamin.
One large (50.3g) egg provides 1.24 mcg of vitamin D (13).
| Egg Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 large egg (50.3g) | 1.24 mcg | 6% DV |
| 100 grams | 2.46 mcg | 12% DV |
13) Eel
While it may not appeal to everyone owing to its appearance, eel is one of the most nutritious types of seafood.
Furthermore, with a cup (136g) serving of cooked eel providing 28.2 mcg of vitamin D, meeting the recommended intake is not difficult (14).
Eel also contains significant amounts of protein, omega-3, and other important vitamins such as vitamin A and vitamin B12.
| Eel Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cup (136g) | 28.2 mcg | 141% DV |
| 100 grams | 20.7 mcg | 104% DV |
14) Fish Roe
As a relatively unusual food in the western diet, fish roe (fish eggs) is not as common as most other seafood varieties.
However, fish roe is incredibly nutritious, and it offers a wide range of essential nutrients.
An ounce (28g) serving, raw weight, of fish roe offers 3.43 mcg of vitamin D (15).
Other reasons to consider fish roe include its important omega-3 content—more than 2.4 grams per 100 grams—and its large supply of vitamin B12.
| Fish Roe Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 oz (28g) | 3.43 mcg | 17% DV |
| 100 grams | 12.1 mcg | 61% DV |
15) Halibut

Halibut is a type of flatfish that lives in the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, and it is a significant source of vitamin D.
Per half fillet (159g) serving, cooked halibut provides 9.22 mcg of the vitamin (16).
In addition to its vitamin D content, halibut is an excellent source of omega-3 and protein.
| Halibut Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1/2 fillet (159g) | 9.22 mcg | 46% DV |
| 100 grams | 5.8 mcg | 29% DV |
16) Herring
Herring is another oily fish that offers many nutritional benefits, including a high content of vitamin D.
Per small (163g) herring fillet, there is a vitamin D content of 8.64 mcg (17).
Other good reasons to eat herring include its ample provision of vitamin B12 and omega-3 fatty acids.
| Herring Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| Small fillet (163g) | 8.64 mcg | 43% DV |
| 100 grams | 5.3 mcg | 27% DV |
17) Orange Juice (Fortified)
As well as being an excellent source of vitamin C, orange juice is another popular food (or drink) product often fortified with vitamin D.
However, fortification of orange juice is not universal, and it depends on the particular product, so check the label carefully.
A 249-gram cup of orange juice fortified with vitamin D may provide 2.49 mcg of the vitamin (18).
| Orange Juice (fortified) Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cup (249g) | 2.49 mcg | 12% DV |
| 100 grams | 1.0 mcg | 5% DV |
18) Pork Spare Ribs
Spare ribs are a cut of pork from around the belly and breastbone.
A three-ounce (85g) serving of spare ribs offers 2.21 mcg of vitamin D (19).
| Pork Spare Ribs Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 oz (85g) | 2.21 mcg | 11% DV |
| 100 grams | 2.6 mcg | 13% DV |
19) Portobello Mushrooms
Providing they were exposed to UV light; portobello mushrooms are another common mushroom that can offer a good amount of vitamin D.
A 121-gram cup of sliced and grilled UV-exposed portobello mushrooms offers 15.9 mcg of vitamin D (20).
| Portobello Mushroom Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cup (121g) | 15.9 mcg | 80% DV |
| 100 grams | 13.1 mcg | 66% DV |
20) Rainbow Trout
With a similar appearance and flavor to salmon, trout is a nutritious fish that provides a significant source of vitamin D.
Per 71-gram fillet, cooked rainbow trout offers 13.5 mcg of vitamin D (21).
| Rainbow Trout Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 fillet (71g) | 13.5 mcg | 68% DV |
| 100 grams | 19.0 mcg | 95% DV |
21) Salami
Although cured meats sometimes get a bad reputation in the media for their salt ad preservative content, they still contain a good range of nutrients.
Salami provides a small amount of vitamin D too. For every two-ounce (56g) serving, salami contains 0.504 mcg of the vitamin (22).
| Salami Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 2 oz (56g) | 0.504 mcg | 3% DV |
| 100 grams | 0.9 mcg | 5% DV |
22) Sardines
Sardines are an excellent source of nutrients for a relatively affordable price.
One of the nutrients sardines provide is vitamin D, with a 92-gram can of sardines offering 4.42 mcg (23).
| Sardines Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 can (92g) | 4.42 mcg | 22% DV |
| 100 grams | 4.8 mcg | 24% DV |
23) Skim Milk
Most processed milk is fortified with vitamin D in the United States. However, this may vary depending on the country in which one resides, so check labels carefully.
According to USDA data, a 246-gram cup of skim milk fortified with vitamin D offers 2.71 mcg of the vitamin (24).
| Skim Milk (fortified) Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cup (246g) | 2.71 mcg | 14% DV |
| 100 grams | 1.1 mcg | 6% DV |
24) Sockeye Salmon
While all varieties of salmon are full of vitamin D, sockeye salmon appears to provide a considerable amount.
Per 155-gram half-fillet, sockeye salmon provides 25.9 mcg of vitamin D (25).
| Sockeye Salmon Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1/2 fillet (155g) | 25.9 mcg | 130% DV |
| 100 grams | 16.7 mcg | 84% DV |
25) Soy Milk (Fortified)
Just like dairy milk is fortified with vitamin D, different plant milk varieties can be too.
In this regard, soy milk fortified with vitamin D provides 2.68 mcg of vitamin D per 244-gram cup serving (26).
| Soy Milk (fortified) Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cup (244g) | 2.68 mcg | 13% DV |
| 100 grams | 16.7 mcg | 6% DV |
26) Swordfish
This guide has shown that fish are some of the highest vitamin D foods.
Swordfish is another rich source, and a 170-gram fillet provides 29.8 mcg (27).
On the negative side, swordfish contains significant concentrations of mercury.
One study noted that people who regularly consume swordfish have blood mercury concentrations “that exceed the tolerable daily intake limits recommended by the World Health Organization” (28).
| Swordfish Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 fillet (170g) | 29.8 mcg | 149% DV |
| 100 grams | 16.7 mcg | 88% DV |
27) Yogurt
As with other milk products, yogurt can be fortified.
USDA data shows that a vanilla, low-fat yogurt fortified with vitamin D will provide 2.94 mcg of the vitamin per 245-gram cup (28).
| Yogurt (fortified) Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cup (245g) | 2.94 mcg | 15% DV |
| 100 grams | 1.2 mcg | 6% DV |
28) Tuna (Bluefin)
Tuna is another good seafood source of vitamin D.
Based on its raw weight, a three-ounce (85g) serving of bluefin tuna has a vitamin D content of 4.84 mcg (29).
However, like swordfish, bluefin tuna is a fish that can contain high amounts of mercury.
| Bluefin Tuna Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 3 oz (85g) | 4.84 mcg | 24% DV |
| 100 grams | 5.7 mcg | 29% DV |
29) Turkey (With Skin)

Turkey provides a small amount of vitamin D. The fatty skin also contains some of the vitamin, so turkey with skin will provide more than just turkey meat.
A three-ounce serving of roast turkey with skin, offers 0.34 mcg of vitamin D (30).
| Roast Turkey Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 3 oz (85g) | 0.34 mcg | 2% DV |
| 100 grams | 0.4 mcg | 2% DV |
30) Whole Milk
According to USDA data, a 244-gram cup of whole milk provides 2.68 mcg of vitamin D (31).
Unlike low-fat milk products, whole milk contains a natural source of vitamin D.
However, this natural content is only minimal, and most of the vitamin D in whole milk still comes from fortification.
A three-ounce serving of roast turkey with skin offers 0.34 mcg of vitamin D (30).
| Whole Milk Serving Size | Vitamin D Content | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 cup (244g) | 2.68 mcg | 13% DV |
| 100 grams | 1.1 mcg | 6% DV |
Don’t Forget Supplements and Sunlight
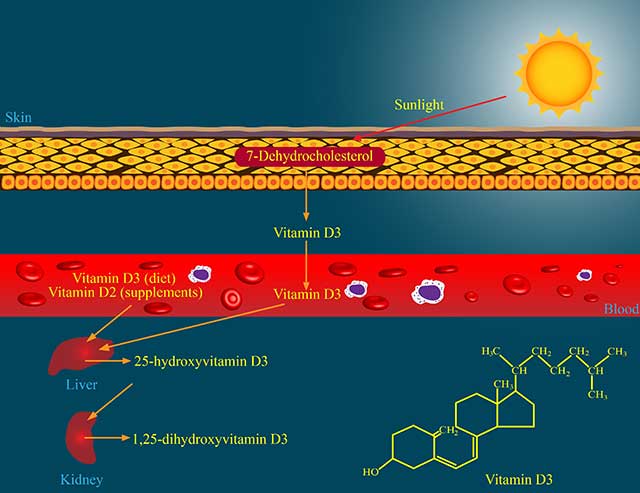
Lastly, it is worth remembering that sunlight, from sensible and safe sun exposure, can provide a high amount of vitamin D.
According to a recent Canadian study, sunlight exposure can produce the recommended vitamin D level in as little as 14 minutes (32).
However, this depended on the sun’s intensity and the individual’s skin color, and the time rose to as high as 58 minutes in people with darker skin tones.
It is also essential to practice good sun-safe habits such as avoiding burning and using sunscreen or covering up when necessary.
Supplements can be another good source of vitamin D, and there are numerous available products.
The two types of vitamin D supplements are D2 and D3.
For further information, here is an evidence-based guide showing how D2 and D3 compare.
Final Thoughts
As shown in this article, there are many different ways to get sufficient vitamin D, and there are various food options.
Although sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D, foods such as halibut, mackerel, and other oily fish offer substantial concentrations of the vitamin.
Dairy, plant milk, and other fortified food products all play a role too.
For more on nutrients, see the best dietary sources of zinc.