Avocado oil has become an increasingly popular cooking oil over the past several years.
However, just how much of a healthy choice is it?
This article examines the science and presents some potential health benefits of using avocado oil.
We also look at the drawbacks and the oil’s nutrition profile.
Nutrition Facts
The table below shows the calorie, macronutrient, and fatty acid profile for avocado oil per tablespoon and per 100 grams (1).
| Calorie/Nutrient | Per Tablespoon | Per 100 g |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 124 kcal | 884 kcal |
| Carbohydrate | 0 g | 0 g |
| Fat | 14 g | 100 g |
| Saturated Fat | 1.6 g | 11.6 g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 9.9 g | 70.6 g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 1.9 g | 13.5 g |
| Omega-3 | 134 mg | 957 mg |
| Omega-6 | 1754 mg | 12531 mg |
| Protein | 0 g | 0 g |
Potential Benefits of Avocado Oil
Based on scientific research, here are some potential health benefits of using avocado oil.
1) Avocado Oil Is Good For High-Heat Cooking
The oxidative stability of cooking oil should be the foremost concern when cooking at a high temperature.
Oxidative stability refers to how stable the oil’s fats are during exposure to heat. For instance, oil with a low degree of oxidative stability can easily break down (and thus oxidize) during cooking.
Unfortunately, oxidized oils generate polar compounds, and these oils have links with several health problems, including an increased cardiovascular risk (2, 3).
On the positive side, avocado oil appears to have reasonably good heat stability thanks to its low proportion of polyunsaturated fat.
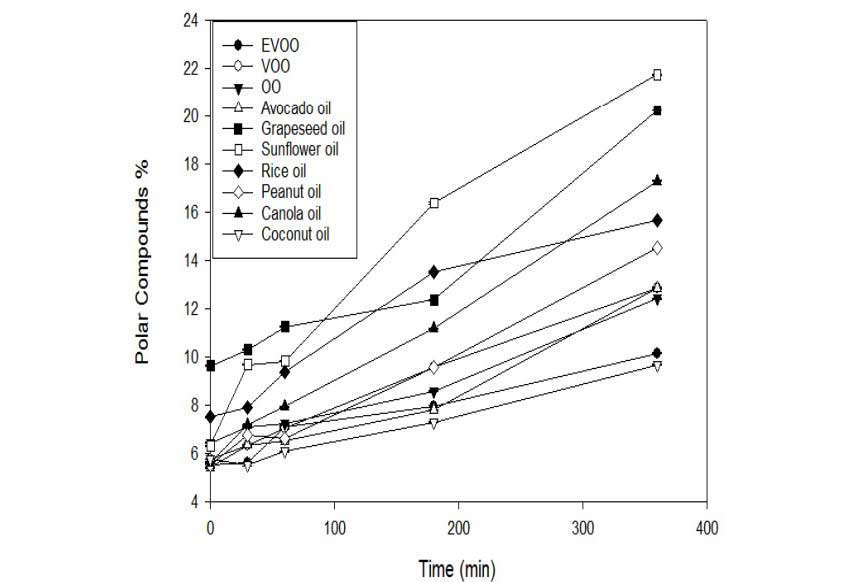
In a recent independent lab analysis, researchers heated ten of the most common cooking oils to a temperature of 180°C (356°F).
The graph below shows the number of polar compounds each oil generated over time (4);
As shown, after 6 hours of heat exposure, avocado oil had generated one of the fewest amounts of polar compounds behind coconut oil, extra virgin olive oil, and regular olive oil.
2) An Excellent Source of Oleic Acid
As shown in the nutrition facts section, avocado oil is approximately 71% monounsaturated fat (MUFA) by weight.
Furthermore, the main monounsaturated fatty acid is oleic acid, accounting for 67% of the oil’s fat content (1).
Oleic acid is one of the most research-backed fatty acids, and the media often refer to it as the “heart healthy” fat in olive oil. Notably, recent studies suggest that oleic acid may protect against insulin resistance and decrease inflammation in the body (5, 6, 7).
In one recent randomized controlled trial, 50 men ate a diet with 39% of energy from fat for thirty weeks. As part of this study, the men followed six different diet designs each lasting five weeks, totaling thirty weeks in total.
Each of the different diets emphasized different fatty acids including trans fatty acids, stearic acid, and various saturated fats. Additionally, one control diet that replaced some of the fat with carbohydrate.
The results showed that the oleic acid diet led to lower levels of inflammatory markers such as interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein (8).
We can see similar results in other cooking oils with high amounts of oleic acid, such as macadamia nut oil.
3) Avocado Oil Has a Mild and Neutral Taste
One benefit that many people appreciate about avocado oil is the taste.
While some coconut and extra virgin olive oils have a strong taste, avocado oil has a very neutral flavor.
As a result, cooking food with avocado oil imparts no strong flavor from the oil, and keeps everything tasting as intended.
For this reason, avocado oil is a popular ingredient for making homemade mayonnaise.
If you want to give this a try, there is a sample recipe here.
4) Avocado Oil Can Enhance Nutrient Bioavailability
This does not only apply to avocado oil, and any source of dietary fat will enhance the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
However, specific studies show that avocado oil has positive results in increasing nutrient bioavailability.
In one study, healthy men and women consumed salad and salsa either with or without avocado oil (9).
The results showed that eating the salad and salsa alongside 24 grams of avocado oil enhanced the absorption of vitamin A carotenoids alpha-carotene by 7.2 times, beta-carotene by 15.3 times, and lutein by 5.1 times.
Avocado oil should also have this effect on other fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin K1 (found predominantly in green vegetables).
5) May Help To Lower Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress refers to a situation when the body is overwhelmed by the production of free radicals and cannot attenuate their damaging effects.
There are many potential causes of oxidative stress, and these can include unhealthy foods, environmental pollutants, smoking, and several other factors (10).
Over time, oxidative stress can damage our cells and DNA, potentially leading to chronic diseases over the long-term (11).
Interestingly, numerous studies in diabetic or hypertensive rats demonstrate that avocado oil decreases oxidative stress (12, 13, 14).
However, we cannot automatically assume animal study outcomes would apply to humans, and this requires confirming by evidence from human trials.
6) Rich Source of Vitamin E
Vitamin E is an important fat-soluble vitamin that acts as an antioxidant in the body.
However, it can be hard to get enough of this vitamin, and it does not occur in significant proportions in many foods.
Currently, the reference daily intake (RDI) for the vitamin is set at 15 mg for anyone over the age of 15 (15).
Studies show that avocado oil contains around 24.5 mg of vitamin E per 100 grams, which works out at around 3.5 mg per tablespoon (16).
Antioxidant vitamins like vitamin E can help to reduce free radical damage in the body. With this in mind, an adequate vitamin E intake may be protective against inflammation-related chronic disease (17).
7) Contains Eye-Protective Antioxidants
First of all, avocado oil is a good source of the eye-protective antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin (18, 19).
Studies show that these two carotenoid compounds may improve (or potentially prevent) macular degeneration.
Additionally, research suggests that low levels of plasma lutein and zeaxanthin are associated with numerous retinal diseases and age-related cataracts (20, 21).
Avocado Oil Drawbacks
While there are no major concerns about avocado oil, there are some slight drawbacks.
1) Not as Heat-Stable As Some Other Oils
As we saw earlier, avocado oil is reasonably heat-stable for use as cooking oil.
However, it doesn’t quite match up to coconut oil and the various olive oils. With that said, this is not necessarily a “bad” thing, and all of these oils are still healthy options.
Additionally, unlike extra virgin olive oil, avocado oil contains very few polyphenols. These compounds are associated with a range of potential benefits, and they are one reason why extra virgin olive oil may offer better oxidative stability (22).
2) Avocado Oil Is Expensive Compared To Other Oils
Another negative point is that avocado oil is frequently overpriced, and depending on location, it can be expensive to source.
As more avocado oils have become available, the price has fallen quite a lot over the past few years, and this trend should continue.
However, it does tend to be more expensive than both coconut oil and extra virgin olive oil (which both have a larger evidence-base).
Final Thoughts
Overall, avocado oil is one of the healthier cooking oil choices.
The current research on avocado oil isn’t as extensive as the research on extra virgin olive oil, but it seems to be a reasonably good oil.
It stands up to heat well, it has a mild flavor, and it may potentially have several health benefits.
If you’re looking for neutral-tasting cooking oil that performs well at high temperatures, avocado oil might be the perfect fit.
On the other hand, if you want an oil with the most evidence behind it, extra virgin olive oil is probably the better option.
For more on cooking oils, see this review of peanut oil.




What about the omega6 to omega3 ratio, are you happy to overlook that ?
Providing people are getting enough omega-3 in the first place (i.e. oily fish) then I don’t think it matters – it is quite low in a regular serving size anyway.