Water chestnuts are a food that many people recognize without knowing a lot about them.
What are they? What do they offer nutritionally? How can we use them?
This article examines the characteristics, nutritional values, and potential benefits of water chestnuts.
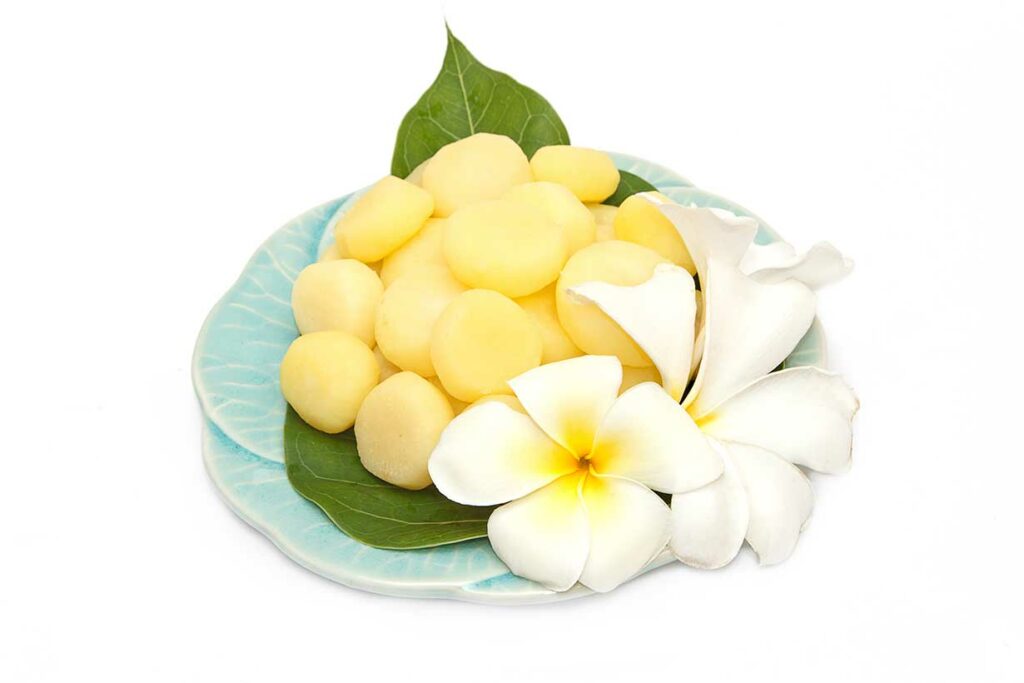

Table of contents
What Are Water Chestnuts?
Firstly, water chestnuts are also known as Chinese water chestnuts and by their scientific name of ‘Eleocharis dulcis’.
Despite their name, water chestnuts are not similar to regular chestnuts in anything other than appearance, nor are they a type of nut.
Instead, water chestnuts are a kind of tuber that grows in ponds, marshes, and other aquatic environments.
In other words, water chestnuts are small aquatic vegetables, and they have a chestnut-shaped white flesh surrounded by dark brown skin.
After peeling, the inner flesh of water chestnuts can be cooked, and it offers a crunchy and flavorful addition to any dish.
In terms of appearance, cooked water chestnuts look slightly like baby/new potatoes.
Canned water chestnuts are easy to find, and they are usually packed and sold pre-sliced. However, it can be more challenging to find fresh water chestnuts than canned products.
How Do They Taste?
Water chestnuts have a crunchy texture and a unique, slightly sweet flavor.
Interestingly, water chestnuts do not get softer like other vegetables during cooking, and they retain their crunch.
As a result, the texture of water chestnuts adds a nice variety to many dishes, and the vegetable offers a satisfying pear-like crunch.
Nutrition Facts For Water Chestnuts
Here are the nutritional values for raw water chestnuts per 3.5 oz (100-gram) serving.
The source of nutritional data is the NCCDB nutrition database (1). All daily values have been calculated using the nutrition data and the FDA’s published daily values (2).
| Name | Amount | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 97 kcal | |
| Carbohydrates | 23.94g | 9% DV |
| Fiber | 3.0g | 11% DV |
| Sugars | 4.80g | |
| Fat | 0.10g | <1% DV |
| Saturated | 0.03g | <1% DV |
| Monounsaturated | 0.01g | |
| Polyunsaturated | 0.04g | |
| Omega-3 | 0.01g | |
| Omega-6 | 0.03g | |
| Protein | 1.40g | 3% DV |
Vitamins
- Vitamin B6: 19% of the daily value (% DV)
- Riboflavin (B2): 15% DV
- Thiamin (B1): 12% DV
- Pantothenic acid (B5): 10% DV
- Vitamin E: 8% DV
- Choline: 7% DV
- Niacin (B3): 6% DV
- Vitamin C: 4% DV
- Folate: 4% DV
- Vitamin K: <1% DV
Minerals
- Copper: 37% DV
- Manganese: 14% DV
- Potassium: 12% DV
- Phosphorus: 5% DV
- Magnesium: 5% DV
- Zinc: 5% DV
- Calcium: 1% DV
- Selenium: 1% DV
- Sodium: 1% DV
- Iron: <1% DV
Additional Details
- Water chestnuts have a water content of 73%
- They have a low oxalate content (2.42 mg per 100g)
Water Chestnuts Are Nutrient-Dense
As shown in the nutritional values, water chestnuts are a good source of numerous essential vitamins and minerals.
For instance, per 100 grams, water chestnuts provide more than 10% of the daily value for:
- Thiamin (B1)
- Riboflavin (B2)
- Vitamin B5
- Vitamin B6
- Copper
- Manganese
- Potassium
This large amount of nutrients in a portion of water chestnuts equal to only 97 calories demonstrates how nutrient-dense the vegetable is.
Rich Source of Flavonoid Polyphenols
Water chestnuts contain high concentrations of flavonoids and phenolic acids (3, 4).
Flavonoids and phenolic acids are polyphenols found in foods like berries and cocoa. Polyphenols are bioactive compounds capable of influencing the human body (5).
Cell (test tube) studies using extracts of water chestnut have demonstrated antioxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-diabetic effects (6, 7).
That said, it is vital to be clear on what this does—and doesn’t—show. First, it does show that water chestnuts contain some potentially beneficial compounds.
However, we cannot use these studies to make any strong claims about the effects of water chestnuts in humans.
This is because exposing cells to an extract in a test tube will be very different from what happens in the human body from eating the food itself.
At present, there is a lack of human trials using water chestnuts, so any strong claims about their effects require a pinch of salt.
Potential Visual Benefits
A 2018 randomized controlled trial investigated the impact of a supplement containing water chestnut extract and lutein on visual function (8).
Lutein is a carotenoid with importance for visual function, and water chestnut was selected by the researchers for its “potentially active ingredients.”
In the study, 110 participants with visual fatigue were given either the supplement (n=55) or a placebo (n=55) for 12 weeks.
Over the 12 weeks, significant changes from baseline were seen in the supplement group compared to placebo for markers of visual function.
Additionally, a 2020 animal study investigated lutein and water chestnut extract for potential use in inhibiting cataract development (9).
The study results showed that, in rats, the water chestnut and lutein extract delayed the onset of cataracts. Discussing the study, the researchers concluded that “simultaneous administration of lutein and water chestnut extract may delay age-related cataracts by reducing oxidative stress and glycative stress.”
These studies are interesting but preliminary, and further human research is necessary to ascertain any potential benefit.
Why Do Water Chestnuts Stay Crunchy After Cooking?
As previously mentioned, water chestnuts have the interesting characteristic of staying crunchy even after cooking (10).
There is often a clear texture difference between raw and cooked vegetables.
For example, many vegetables soften with cooking, like carrots, onions, and potatoes, making water chestnuts unique in this regard.
For those interested in knowing why water chestnuts stay crunchy, it is because their cell walls contain significant amounts of polyphenols.
Specifically, a phenolic acid called 8,8′-diferulic acid appears to be concentrated in the cell walls of water chestnuts. This compound contributes to cell adhesion (cells attaching to each other) and creates a crunchy texture (11).
How To Use Water Chestnuts
There are many different ways to use water chestnuts. Among these, they work particularly well as a crunchy addition to stir-fries and noodle-based dishes.
Here is a full list of ideas for using these crunchy vegetables:
- Add them to stir-fries
- Mix them into noodle and rice-based dishes
- Use them as a crunchy addition to a salad
- Add them to casseroles, soups and stews
- Use them on kebab sticks to offer a different texture experience. E.g: marinated chicken, pineapple, water chestnuts, garlic, peppers
In truth, water chestnuts do not have an overbearing flavor, and they will work well in most recipes.
Common Questions
No, water chestnuts are an aquatic (water) vegetable. They grow in aquatic environments.
No, canned chestnuts have already been pre-cooked and do not need cooking again. Whether one wishes to reheat them or not is a taste preference more than anything else.
Water chestnuts are not a nut, and there is no reason for people with a tree nut allergy to avoid them. However, as with any food, there is always the possibility of a (rare) allergy to water chestnuts.
It can be much harder to find fresh water chestnuts than canned products on store shelves. However, Asian grocery stores are an excellent place to look, and some may carry fresh water chestnuts. Aside from Asian grocery stores, local online delivery options might be worth researching.
Final Thoughts
Water chestnuts are not a standard part of diets in Western countries.
However, they have many positive characteristics, covering both nutritional value and taste.
These little aquatic vegetables can add a lot of nutrients for minimal calories, and they help enhance the taste of numerous dishes.