People often use low-carb diets to try to lose weight, but what if someone enjoys this way of eating and wishes to gain weight?
Given how most nutrition articles focus on low-carb diets for fat loss, what about using them for gaining weight?
The usual advice for weight gain is just to eat a higher amount of carbohydrates to “bulk up,” but that method isn’t really compatible with a diet low in carbohydrates.
In this article, we will examine how someone may attempt to gain weight with a low carb diet.
Table of contents
- The Fastest Way To Gain Weight Isn’t Necessarily the Best
- Optimal Nutrition to Support Weight Gain
- How To Gain Weight With Nutritious Low-Carb Food Choices
- How to Gain Weight and Muscle on a Low-Carb Diet?
- Resistance Training and Heavy Lifting For Weight Gain
- Do Sleep and Stress Affect Weight Gain?
- 10 Quick Low-Carb Weight Gain Tips
- Final Thoughts

The Fastest Way To Gain Weight Isn’t Necessarily the Best
First of all, wanting to gain weight quickly is understandable. However, it can often detract from gaining weight in a healthy and sustainable manner. In other words, slow and steady usually wins the race.
Ultra-high calorie bulking diets are very common, and they can work very well for quick weight gain for some people. But usually, these people are extremely active bodybuilders or athletes who don’t mind gaining a little fat in addition to muscle.
With this kind of diet, people tend to load up on hundreds of extra calories and grams of carbohydrates per day. While this method works, it usually comes with a varying amount of fat gain depending on how well (or not) the diet was formulated.
And for some people, this extra fat tissue can be difficult to lose. Therefore, there can be a difference between gaining weight in the fastest way and increasing size in the healthiest way possible.
Over the next few sections, we will look at some ways in which we can progressively increase our weight, in a healthy way, using a low-carb diet.
Optimal Nutrition to Support Weight Gain
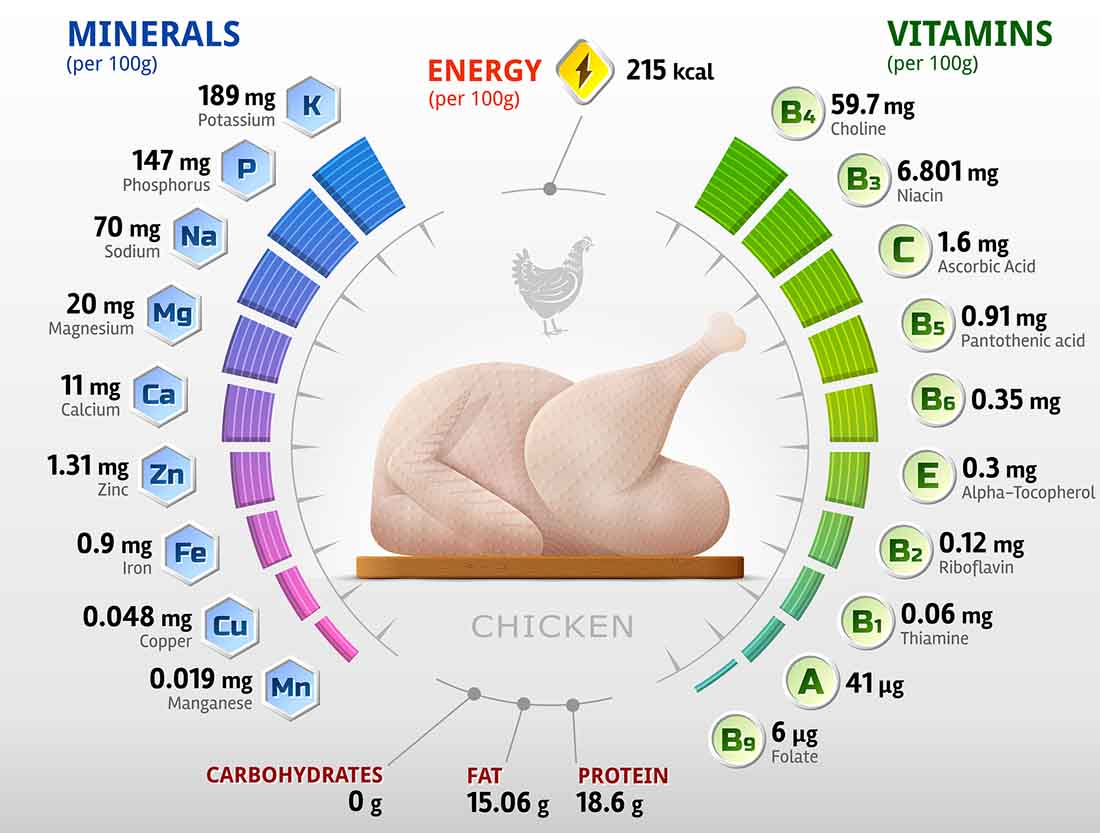
As with any way of eating, for overall health, it is important to formulate a nutrient-rich diet that supplies a good amount of beneficial nutrients and doesn’t result in overconsumption of nutrients we should limit, like sodium and saturated fat.
As a quick example, the nutritional properties from 500 calories of white bread and butter are very different from 500 calories of fish, spinach, and sweet potato.
Yes, they have the same energy density, but the nutrient content is entirely different.
For instance, white bread and butter provide refined carbohydrates, saturated fat, salt, and a small amount of essential nutrients. On the other hand, a serving of fish, sweet potato, and spinach offers significant quantities of protein, magnesium, vitamin A, potassium, and omega-3, just to name a few beneficial nutrients.
A Sufficient Energy Intake Is the Key
Just as as the health properties of a diet depend on its nutrient composition, the ability to gain weight depends on energy density.
However, this doesn’t mean that we should run out to the shops and buy a tub of ice cream, fried chicken, and wash them down with two liters of soda. Ideally, a low-carb diet for weight gain should emphasize nutrient-rich foods.
That said, it is worth noting that low-carb diets are not the ideal diet for weight gain since they restrict many high-carbohydrate, high-calorie foods. However, we’ll take a look at some of the more energy-dense low-carb food options in this guide.
How To Gain Weight With Nutritious Low-Carb Food Choices

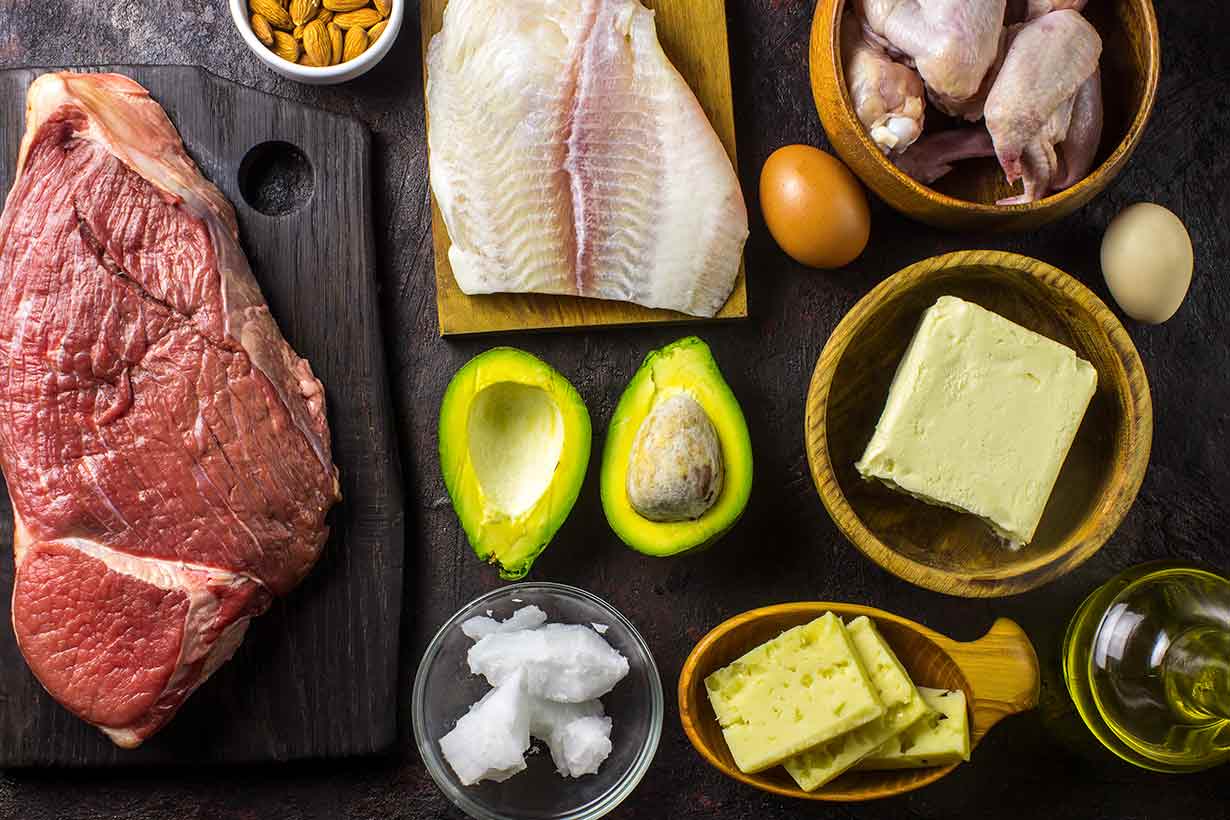
First of all, the cornerstone of a well-formulated low-carb diet is similar to any other diet: minimally processed, nutrient-rich foods.
On this note, whole foods that are compatible with a low-carb way of eating include:
- Dairy such as cheese, milk, and yogurt
- Eggs
- Fish and seafood in general
- Fruit (especially low-sugar options like avocado, olives, berries)
- Meat and organ meats
- Nuts
- Oils
- Seeds
- Vegetables
However, among these nutritious food groups, if we want to encourage weight gain, we should emphasize the most energy-dense of these foods.
Meat

While lean meat is often a popular choice, it is fattier cuts of meat that offer the most energy.
Here are some of the more energy-dense meats:
- Bacon
- Beef (ribs are particularly good)
- Chicken (including skin)
- Lamb
- Pork (of all varieties – pork belly included)
- Sausages
- Steak
However, it is important to be aware that these options tend to be higher in saturated fat—overconsumption of this fatty acid can lead to elevations in LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) levels, which are linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (1, 2).
In this context, while Dietary Guidelines advise opting for leaner cuts of meat, it is the overall dietary pattern that matters most rather than one specific food choice. For example, a diet can include a source of fatty meat while also habitually following guidelines on saturated fat intake and including a variety of unsaturated fats.
On this note, public health organizations recommend that saturated fat intake is limited to a maximum of 10% of total calories, which is 200 calories based on a 2000-calorie diet, equal to approximately 22 grams of saturated fat (3, 4).
Fish

Similar to meat, oily species of fish offer much higher energy-density than lean fish.
On the positive side, as well as being very energy-dense, oily fish is the best dietary source of essential omega-3 fatty acids (5, 6).
Some excellent options include:
- Anchovies
- Herring
- Mackerel
- Salmon
- Sardines
- Trout
Not only are these fish significant sources of omega-3, but they also have some of the lowest mercury concentrations among commercial fish (7).
Note: Some larger oily fish, such as shark, swordfish, and tuna, can contain high levels of mercury (7).
Dairy

Dairy-based foods are typically nutrient-rich and many options are highly energy-dense.
The following dairy foods are all calorie-dense options for a weight-gaining diet:
- Butter
- Cheese
- Cream
- Ghee
- Milk
- Yogurt
Once again, it is important to be aware these foods can contain high levels of saturated fat.
Nuts and Seeds
Not only are nuts and seeds a rich source of essential nutrients, but they are also among the most energy-dense foods.
For example, here is the calorie (kcal) content for several popular nuts and seeds per 100 grams (8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14):
- Almonds: 626 kcal
- Peanuts: 567 kcal
- Pecans: 750 kcal
- Walnuts: 730 kcal
- Chia seeds: 486 kcal
- Pumpkin seeds: 574 kcal
- Sunflower seeds: 582 kcal
As this shows, nuts and seeds are incredibly rich in energy, making them a low-carb friendly food for weight gain.
Furthermore, nuts and seeds contain high levels of unsaturated fats, which are thought to be beneficial for cardiovascular health. Systematic reviews indicate that nuts and seeds can lower LDL-C and are associated with a likely reduced risk of cardiovascular disease (15, 16, 17).
Vegetables

All vegetables are a great addition to the average diet, but on a low-carb diet for weight gain, there’s a choice to make regarding starchy vegetables like potatoes, sweet potatoes, and other root vegetables.
These tend to be higher in carbohydrates. Adding starches to a calorie-dense diet full of healthy fat will increase the speed of weight gain, which for a weight-gaining diet is a good thing.
However, this may depend on how ‘low-carb’ someone prefers their diet to be.
Remember, “low-carb” doesn’t mean “no-carb.” In a consensus report on nutrition therapy for adults with diabetes or prediabetes, a “low-carb” diet was defined as containing 26-45% of calories from carbohydrates (18).
This same report defined very-low-carb diets as containing less than 26% of calories from carbohydrates, but noted that such diets often have a 20-50 gram daily carbohydrate target for the purpose of inducing ketosis. This amount would be equal to less than t10% of calories based on a 2000-calorie diet.
Understandably, very-low-carb diets may make it harder to gain weight.
Fruit
As well as being high in nutrients, avocados are very energy-dense, with a 200-gram avocado providing over 300 calories (19).
For those who are happy with a more moderate low-carb dietary pattern, fruits like bananas, mango, and pineapple are also among the highest-energy options.
Plant Oils

There is a broad range of plant-based fats that you can add to a low-carb diet.
Some of these oils include:
- Avocado oil
- Canola oil
- Extra virgin olive oil
- High oleic oils
- Peanut oil
- Sesame oil
- Soybean oil
- Sunflower oil
These oils are all incredibly energy-dense, containing over 120 calories per tablespoon (20, 21, 22).
As well as helping to increase the calorie content of the diet, these oils may also confer health benefits.
For instance, systematic reviews indicate that canola oil and olive oil improve various markers of cardiovascular health and reduce cardiovascular risk (23, 24).
Drinks

It’s true that ‘liquid calories’ are one of the main sources of excess energy, thereby contributing to the obesity crisis (25, 26).
However, for the purpose of a weight-gaining diet, these extra calories from drinks can be useful.
That said, there should be a focus on nutrient-rich drink options rather than sugar-sweetened beverages.
Some good, relatively healthful options—as a source of essential nutrients—include:
- Milk
- Latte
- Protein shakes
- Fresh squeezed juice
- Cocoa-based drinks
How to Gain Weight and Muscle on a Low-Carb Diet?

A diet high in carbohydrates offers advantages for individuals looking to gain muscle/body mass. Furthermore, diets with a higher carbohydrate intake are more scientifically proven for gaining muscle mass and strength than low-carb diets (27).
However, research shows that it is still possible to gain lean body mass on lower-carb diets (28, 29).
Providing the right nutritional requirements to grow are met, it is possible to gain muscle on any diet.
In fact, in their position stand paper on ‘diets and body composition,’ the International Society for Sports Nutrition (ISSN) notes that following a specific diet for lean muscle mass accrual is not important. Further, they point out that a range of dietary systems—from ketogenic and low-carb diets to high-carb, plant-based diets—can be successful (30).
Note: for those wondering how low-carb and ketogenic diets compare, see the key differences here.
Some of the major considerations include:
- Total food intake: There should be a calorie surplus.
- Keep protein high: 1 gram of protein per pound of bodyweight is a good target.
- Try to get sufficient sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours per night.
- Exercise: Regular resistance training helps to stimulate muscle growth.
Increasing Calories
In order to gain weight, we should ideally have a surplus energy intake.
According to the ISSN’s published position stand, “Diets focused primarily on accruing lean mass are driven by a sustained caloric surplus to facilitate anabolic processes and support increasing resistance-training demands.” However, it is important to note that this does not mean we have to eat truly excessive amounts of food as significant calorie surpluses will likely lead to increased fat gain (31).
A variety of useful apps are available to provide estimates of how much food may be necessary to successfully gain weight. For example, Omni Calculator has a useful calculator that can be used to help determine how many daily calories we need to gain weight.
That said, tracking calorie intake isn’t always the right strategy for everyone.
For those with some idea of the nutritional value of different foods, ‘Eat, monitor, and adjust’ is another method that can be helpful, depending on the person.
By this expression, the meaning is just to track progress through the scales and mirror and make small dietary changes dependent upon progress.
Keep Protein High
Protein is the most important of the three macronutrients for increasing lean muscle mass.
In their paper on ‘protein and exercise,’ the ISSN note that 1.4 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day is “sufficient” for most individuals to gain muscle mass (32).
A daily protein intake of 1 gram per pound of body weight would be slightly above the level the ISSN deems ‘sufficient.’
Resistance Training and Heavy Lifting For Weight Gain
Strength training and lifting heavy weights both stimulate muscular growth and have a broad range of benefits for the body in general (33).
While a healthy, optimized diet provides the nutritional building blocks for weight gain, resistance training is necessary for stimulating muscle and increasing lean weight gain.
However, one misconception is that making physical improvements requires an excessive time commitment. The truth is that you don’t need to spend hours at the gym every day.
As a matter of fact, an intense training session two or three times per week is more than enough to stimulate muscle growth.
For individuals with access to a gym, emphasizing “the big three” compound exercises (bench press, deadlifts, and squats) can have large benefits.
These three exercises stimulate growth in a significant number of muscle fibers throughout the body. Research has also shown that squats are an excellent exercise as they increase the secretion of growth hormone (34, 35).
Do Sleep and Stress Affect Weight Gain?

Since our muscles recover and grow during sleep, it’s essential to make sure we spend enough time asleep.
In fact, sleep and stress share an intrinsic connection—several systematic reviews have found associations between sleep deprivation and increased stress levels (36, 37, 38).
Lack of sleep is also associated with increased cortisol levels (39).
In regard to cortisol, research demonstrates that it has catabolic properties. In other words, it breaks down muscle tissue rather than having an anabolic (building) effect (40, 41).
On the subject of sleep, the expert consensus tends to be that 7-9 hours of sleep per night is optimal for most adults (42, 43).
10 Quick Low-Carb Weight Gain Tips
Many people attempt to build muscle, fail, and then conclude that it must be down to their genetics.
While genetics may be true in rarer cases, it’s usually because of common mistakes like not eating enough food.
Adding more energy-dense and protein-dense foods into the diet can quickly remedy this.
Here are some low-carb-friendly ideas that may be helpful in boosting the number of calories you consume each day.
- Replace a drink of water each day with milk.
- Add a protein shake to your breakfast.
- Eat an avocado each day.
- Add a tablespoon of your favorite oil, such as olive oil, to your meal.
- Add milk to your black tea and black coffee, if you drink them.
- Replace lean fish such as cod or haddock with fattier fish like salmon and mackerel.
- If you drink coffee shop Americano, replace it with a latte.
- Have a handful of nuts after each meal.
- If your weight is staying the same, slightly increase portion sizes, monitor, and adjust as appropriate.
- Consider adding more carbohydrates: Emphasize higher-quality, nutrient-rich carbohydrates such as sweet potatoes, pumpkins, and fruit.
For anyone still struggling to gain weight with a low-carb diet, creating an individualized plan with the help of a registered dietitian or qualified nutritionist would likely be a helpful investment.
Final Thoughts
While it can be more difficult to gain weight with a low-carb diet, such dietary patterns can be compatible with gaining lean body mass and overall weight.
However, these diets need to be well-formulated, with careful consideration of the overall diet and how it can meet these goals.
As demonstrated in a 2022 systematic review of the evidence, even very-low-carb ketogenic diets can be used to increase muscle mass “as long as energy surplus is generated” (44).